GAO Report: Cybersecurity - Federal Actions Urgently Needed to Better Protect the Nation's Critical Infrastructure

Recent events—including the ransomware attack on a major U.S. fuel pipeline—illustrate the need to strengthen the cybersecurity of the nation's critical infrastructure.
We testified on the need for the federal government to develop and execute a comprehensive national cyber strategy, and to strengthen the role that it plays in protecting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure. Ensuring the cybersecurity of the nation is on our High Risk List, and we have urged federal agencies to act on it.
If the federal government doesn't act with greater urgency, the security of our nation's critical infrastructure will be in jeopardy.
GAO has previously reported on major cybersecurity challenges facing the nation and the critical federal actions needed to address them (see figure).
Four Major Cybersecurity Challenges and 10 Associated Critical Actions
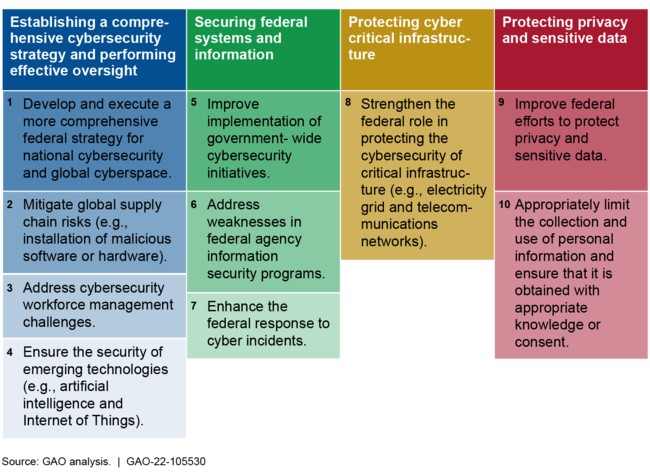
To address critical infrastructure cybersecurity, key actions the federal government needs to take include (1) developing and executing a comprehensive national cyber strategy and (2) strengthening the federal role in protecting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure.
Develop and execute a comprehensive national cyber strategy. In September 2020, GAO reported that the White House's 2018 National Cyber Strategy and related implementation plan addressed some, but not all, of the desirable characteristics of national strategies, such as goals and resources. GAO also reported that it was unclear which official within the executive branch ultimately maintained responsibility for coordinating the execution of the National Cyber Strategy. Accordingly, GAO recommended that the National Security Council update the cybersecurity strategy and for Congress to consider legislation to designate a position in the White House to lead such an effort.
In January 2021, a federal statute established the Office of the National Cyber Director within the Executive Office of the President. In June 2021, the Senate confirmed a Director to lead this new office. In October 2021, the National Cyber Director issued a strategic intent statement, outlining a vision for the Director's planned high-level lines of efforts. The establishment of a National Cyber Director is an important step toward positioning the federal government to better direct activities to address the nation's cyber threats. Nevertheless, GAO's recommendation to develop and execute a comprehensive national cyber strategy is not yet fully implemented. As a result, a pressing need remains to provide a clear roadmap for addressing the cyber challenges facing the nation, including its critical infrastructure.
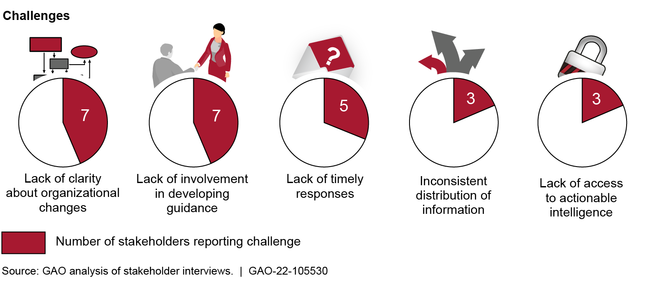
Strengthen the federal role in protecting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure. Pursuant to legislation enacted in 2018, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) within the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) was charged with responsibility for, among other things, enhancing the security of the nation's critical infrastructure in the face of both physical and cyber threats. In March 2021, GAO reported that DHS needed to complete key activities related to the transformation of CISA, including finalizing the agency's mission-essential functions and completing workforce planning activities. GAO also reported that DHS needed to address challenges identified by selected critical infrastructure stakeholders, including having consistent stakeholder involvement in the development of related guidance (see figure). Accordingly, GAO made 11 recommendations to DHS. As of November 2021, DHS had not yet implemented them, though it stated its intent to do so.
Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Coordination Challenges Reported by Stakeholders Representing the 16 Critical Infrastructure Sectors
Regarding specific critical infrastructure sectors, since 2010 GAO has made about 80 recommendations to enhance the cybersecurity of these sectors and subsectors, including within the aviation and pipeline industries. In October 2020, GAO reported that, although the Federal Aviation Administration had established a process for certification and oversight of U.S. commercial airplanes, it had not prioritized risk-based cybersecurity oversight or included periodic testing as part of its monitoring process, among other things. In July 2021, GAO testified that the Transportation Security Administration had not fully addressed pipeline cybersecurity-related weaknesses that GAO had previously identified, such as aged protocols for responding to pipeline security incidents. Until GAO's recommendations to address issues such as these are fully implemented, federal agencies will not be effectively positioned to ensure critical infrastructure sectors are adequately protected from potentially harmful cybersecurity threats.









