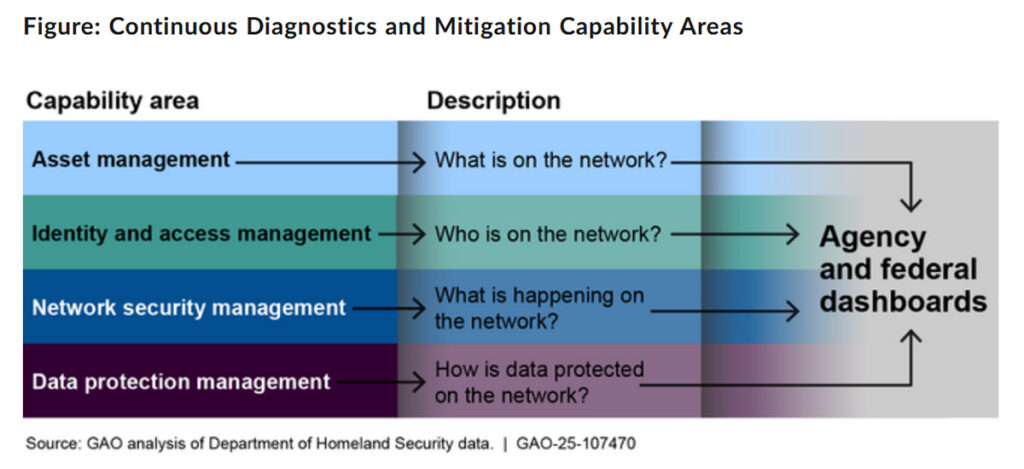
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) are essential in enhancing security across various environments, including critical infrastructure. In its new White Paper, CoESS, the European Private Security Employers’ Representation, demonstrates how collaboration between Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) and Private Security Companies (PSCs) can strengthen overall security and societal resilience.
The paper draws on theoretical sources and showcases best practices to highlight the benefits of PPPs but also describe the challenges that hinder their effectiveness. It offers recommendations for all stakeholders involved to overcome barriers, implement key success criteria and optimise the potential of PPPs. The White Paper is jointly published by CoESS and its Dutch member, Nederlandse Veiligheidsbranche, with the support of the International Security Ligue.
The White Paper was officially launched at the European Security Summit, on 10 October 2024 in The Hague.
This article outlines the key takeaways from the White Paper, which will drive the policy and advocacy actions of CoESS, among others when contributing to EU policies such as the Preparedness Union and the Internal Security Strategy.
An Opportunity for Complementarity and Increased Efficiency
Public-Private Partnerships considered in this paper are all forms of cooperation between LEAs and PSCs. As such, they combine the strengths and resources of public security forces with the specialized capabilities of private security companies. This collaboration addresses complex security challenges efficiently, ensuring a comprehensive approach to the protection of people, assets and infrastructure, and thus society as a whole. The synergy allows for an extended security reach, leverages advanced technologies, and enhances the strategic allocation of resources across the security spectrum.
Significance and Impact
PPPs are shown to optimize the use of resources, allowing LEAs to focus on their core tasks while PSCs address the prevention and detection dimensions. The partnerships enhance operational capabilities, provide scalability in response to changing security demands, and introduce innovative solutions to security management. This strategic collaboration leads to improved flexibility in operations and a proactive stance in security planning.
Highlights
Surprisingly, PPPs are legally possible in only 9 out of 27 EU Member States and mostly in Western European countries, where they cover different realities. While some Member States have advanced partnerships based on formal frameworks, others are informal, local and temporary. The type of protected objects and events also vary, as do the missions that are given to the PSCs.
There is a correlation between the level of professionalism of the industry, the maturity of the legal framework, and the depth of cooperation between LEAs and PSCs. The White Paper describes the advantages in operating PPPs, including:
• Resource Efficiency: Private companies support LEAs by handling preventive and surveillance tasks, freeing up public resources for LEAs to concentrate on their core missions.
• Advanced Specialization: PPPs bring state of-the-art technology and specialized skills, particularly valuable in areas in which they have developed particular know-how, such as access control, distance surveillance and monitoring, protecting certain infrastructure (critical and others), etc.
• Strategic Flexibility: The ability to dynamically scale security measures in response to situational analyses enhances both proactive and reactive capabilities.
Implications for the Security Landscape
The increased complexity and diversity of threats require a shift towards a more integrated and responsive security framework. This approach not only improves immediate responses to threats but also supports a sustained security strategy that adapts to future challenges. The implications extend beyond immediate security enhancements, suggesting long-term benefits in public safety and trust.
Challenges and Strategies for Overcoming Obstacles in PPPs
While Public-Private Partnerships offer substantial benefits, they also face specific challenges that can hinder their effectiveness. Key obstacles include issues of trust and information sharing, differing operational cultures between public and private entities, and regulatory constraints that can stifle collaborative efforts.
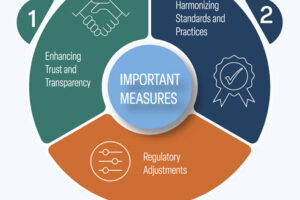
To overcome these challenges, the White Paper recommends several measures, of which the following are particularly important:
1. Enhancing Trust and Transparency: Building trust is fundamental. Initiatives such as joint training sessions, shared operational planning, and regular stakeholder meetings can foster a mutual understanding and strengthen trust. Clear communication and transparency in operations and decision-making processes are crucial for developing a reliable partnership.
2. Harmonizing Standards and Practices: Developing common standards and practices across public and private sectors within PPPs can alleviate cultural and operational discrepancies. Areas to look into may include training, security protocols, data interoperability, vulnerability assessments and complementarity in response strategies to optimise cooperation.
3. Regulatory Adjustments: Modifying existing laws and regulations to support PPP frameworks and allow for the exchange of information between PSCs and LEAs is essential. Legislation should support best value procurement, collaborative actions and facilitate rather than inhibit information sharing, ensuring that both public and private entities operate under a supportive legal framework that will help reinforce mutual trust and promote cooperation. Finally, legislation should also provide that LEAs have a good understanding of what PSCs can and can’t do. This could be included in basic LEA staff training.
By addressing these challenges through targeted strategies, PPPs can not only enhance their operational effectiveness but also achieve a more resilient and adaptive security infrastructure. These efforts require ongoing commitment and adaptation from all stakeholders involved to ensure the continued success and evolution of PPPs in the security sector.
In conclusion, Public-Private Partnerships are indispensable in the modern security apparatus. By effectively combining the unique strengths of LEAs and PSCs, PPPs not only enhance current security measures but also prepare organizations for emerging threats. This White Paper supports the continued development and refinement of PPP frameworks to maximize their positive impact on public security.
About the Author:
Catherine Piana is the Director General of both CoESS and the Aviation Security Services Association – international (in short ASSA-i) and the co-owner and Managing Director of the internationally acclaimed e-learning platform on the Insider Threat, Help2Protect.
The White Paper can be downloaded free of charge at https://coess.org