Nuclear Security: DOE Should Take Actions to Fully Implement Insider Threat Program

The theft of nuclear material and the compromise of information could have devastating consequences. Threats can come from external adversaries or from "insiders," including employees or visitors with trusted access. In 2014, DOE established its Insider Threat Program to integrate its policies, procedures, and resources. The program also coordinates analysis, response, and mitigation actions among DOE organizations.
The House report accompanying a bill for the National Defense Authorization Act for fiscal year 2022 includes a provision for GAO to review DOE's efforts to address insider threats with respect to the nuclear security enterprise. This report examines (1) the extent to which DOE has implemented required standards to protect the nuclear security enterprise from insider threats and (2) the factors that have affected DOE's ability to fully implement its Insider Threat Program.
GAO reviewed the minimum standards and best practices for federal insider threat programs, DOE documentation, and four assessments by independent reviewers. GAO also interviewed DOE and National Nuclear Security Administration officials and contractors.
The Department of Energy has several programs to ensure proper access to and handling of the nation's nuclear weapons and related information. DOE started a program in 2014 to further protect against insider threats from employees, contractors, and trusted visitors.
But as of 2023, DOE hasn't fully implemented the program. For example, DOE doesn't ensure that employees are trained to identify and report potential insider threats. Also, the agency hasn't clearly defined contractors' responsibilities for this program.
DOE changed the program's leadership in February 2023, but there's more to do. We recommended ways to improve the program.
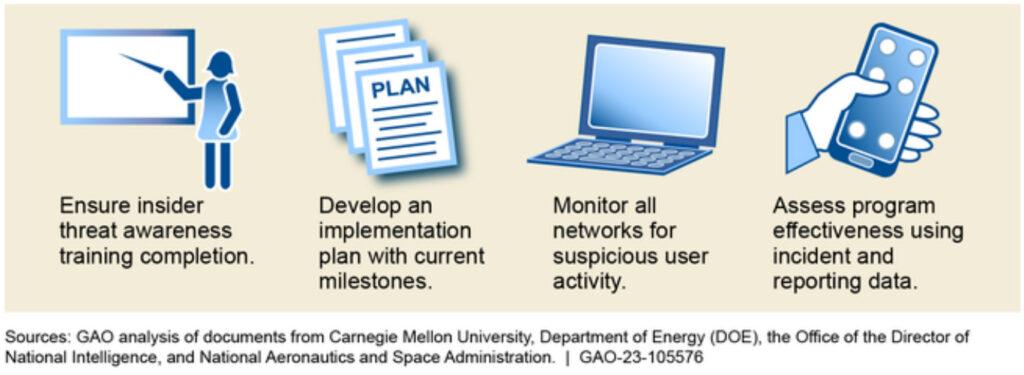
The Department of Energy (DOE) has not implemented all required measures for its Insider Threat Program more than 8 years after DOE established it in 2014, according to multiple independent assessments. Specifically, DOE has not implemented seven required measures for its Insider Threat Program, even after independent reviewers made nearly 50 findings and recommendations to help DOE fully implement its program (see fig. for examples). DOE does not formally track or report on its actions to implement them. Without tracking and reporting on its actions to address independent reviewers' findings and recommendations, DOE cannot ensure that it has fully addressed identified program deficiencies.
Examples of Selected Recommendations from Independent Assessments of DOE's Insider Threat Program
DOE has not fully implemented its Insider Threat Program due to multiple factors.
- DOE has not integrated program responsibilities. DOE has not effectively integrated Insider Threat Program responsibilities. Instead, DOE divided significant responsibilities for its program between two offices. Specifically, the program's senior official resides within the security office, while operational control for insider threat incident analysis and response resides within the Office of Counterintelligence—a part of the organization with its own line of reporting to the Secretary of Energy. Without better integrating insider threat responsibilities between these offices, DOE's insider threat program will continue to face significant challenges that preclude it from having an effective or fully operational program.
- DOE has not identified and assessed resource needs. DOE has not identified and assessed the human, financial, and technical resources needed to fully implement its Insider Threat Program. Program funding identified in DOE's budget does not account for all program responsibilities. For example, DOE's budget does not include dedicated funding for its contractor-run nuclear weapons production and research sites to carry out their responsibilities for implementing the program. Unless DOE identifies and assesses the resources needed to support the Insider Threat Program, it will be unable to fully ensure that components are equipped to respond to insider threat concerns, potentially creating vulnerabilities in the program.

